Electronic seals for document security.
Secure the authenticity and integrity of your documents.
What is an electronic seal?
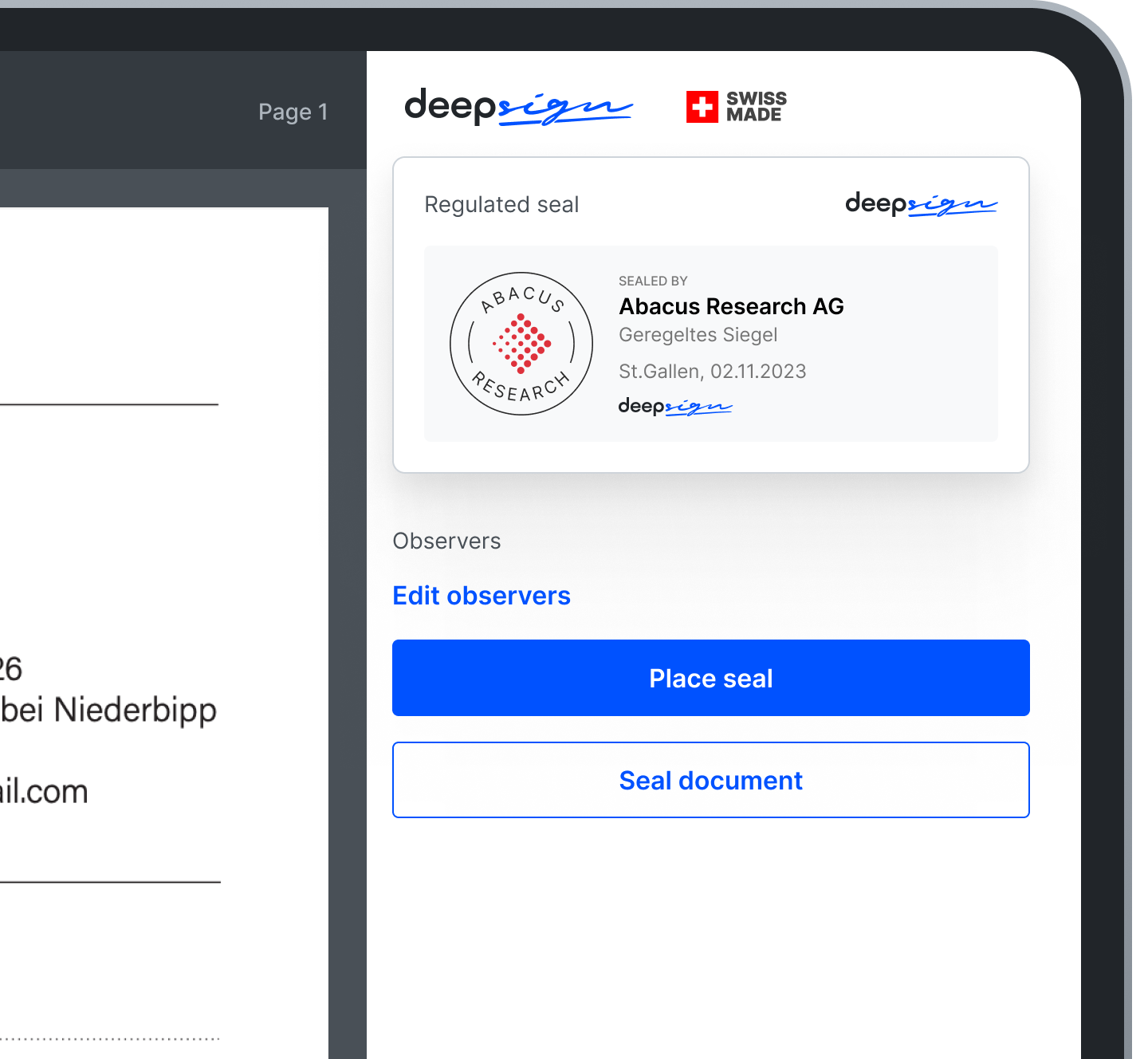
An electronic seal, also known as digital seal or eSeal, is the digital equivalent of the classic company rubber stamp.
An electronic seal is based on a digital signature which is associated with a legal entity (organisations or institutions) and used to ensure the proof of the origin, authenticity and integrity of the entity’s documents.
Your digital seal from DeepSign benefits from integration with our own digital identity app DeepID, which makes it easier for your organisation to be verified and enable the seal.
A single electronic seal that says it all.
Authenticity
Integrity
Your electronic seal in accordance with the law.
With DeepSign you can create two types of electronic seals: advanced and qualified or regulated seals.
Choose the seal that meets your organisation’s needs.
Every organisation has its own particular requirements and needs. Explain yours to us and we will be happy to show you the solution that best suits you.
Compliant with Swiss and EU regulations.
DeepSign electronic seals are compliant with both Swiss and EU regulations, so you can secure your documents regardless of where your company is based.
ZertES
The Federal Act on Electronic Signatures defines the requirements for digital certificates and the obligations of service providers to “promote a wide range of secure certification services” in Switzerland.
eIDAS
The Electronic Identification, Authentication and Trust Services regulation “establishes the framework to ensure that electronic interactions between businesses are safer and more efficient” in the EU.


